Learning ROS. Part 1
1. A Gentle introduction to ROS
My background is Computer Vision and i love it. But recently, my work changed a little bit and now i have to work with both Computer Vision and Robotics. So i have to learn ROS to work with some kinds of Robot Arm and so on.
Personally i found the ROS tutorial is flooded with information and very hard to follow. Beginner level came up with 20 small tutorial, each tutorial has length like several A4 pages. The worst part is there isn’t any top-down architecture expaining. So learning will take weeks and kill beginner’s patience very fast.
I wrote down my learning experience here. First, to clarify and summarize what i learned. Secondly, hope it could help some-one.
1.1. Why ROS is needed ?
A quick read at A Gentle introduction to ROS have me the following points :
ROS is an open-source, meta-operating system for your robot.
It provides the services you would expect from an operating system,
including hardware abstraction, low-level device control,
implementation of commonly-used functionality,
message-passing between processes,
and package management.
It also provides tools and libraries for obtaining,
building, writing, and running code across multiple computer
So ROS is very good at:
- Distributed computation: ROS can use computation resource very effective
- Software reuse: write code once and run on every hardware that support ROS
- Rapid testing: ROS can accelarate the testing process
As i known, currently nearly all of industrial robot maker are using different version of their own operating system. ROS can theorically replace that and make all robot talk in the same language. So it will for sure accelarate the deploying process of robot.
1.2. Install ROS
Just run the following command to install all the needed packages to use ROS.
# get the repo list
sudo sh -c 'echo "deb http://packages.ros.org/ros/ubuntu $(lsb_release -sc) main" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ros-latest.list'
sudo apt-key adv --keyserver hkp://ha.pool.sks-keyservers.net:80 --recv-key 421C365BD9FF1F717815A3895523BAEEB01FA116
sudo apt update
# Install newest ros version: melodic
sudo apt install ros-melodic-desktop-full build-essential
sudo rosdep init
rosdep update
# Load ros environment whenever new terminal is opened
echo "source /opt/ros/melodic/setup.bash" >> ~/.bashrc
# Install required python package
# Customed anaconda environment is not usable
# So we need to use root anaconda environment directly
pip install rosinstall rosinstall-generator wstool rosdep
# rqt tools kit
sudo apt install ros-melodic-rqt ros-melodic-rqt-common-plugins
# add pyside2 to anaconda environment
pip install pyside2 pydot
1.3. ROS’s general concepts
There’s a quick read about ROS’s general concepts at ros-101-intro-to-the-robot-operating-system. ROS is using message queuing architecture, so that’s why ROS’s general architecture is very similar to AMQP ((Advanced Message Queuing Protocol)) architecture (see rabbitmq and medium ). See the following 2 images for comparing.
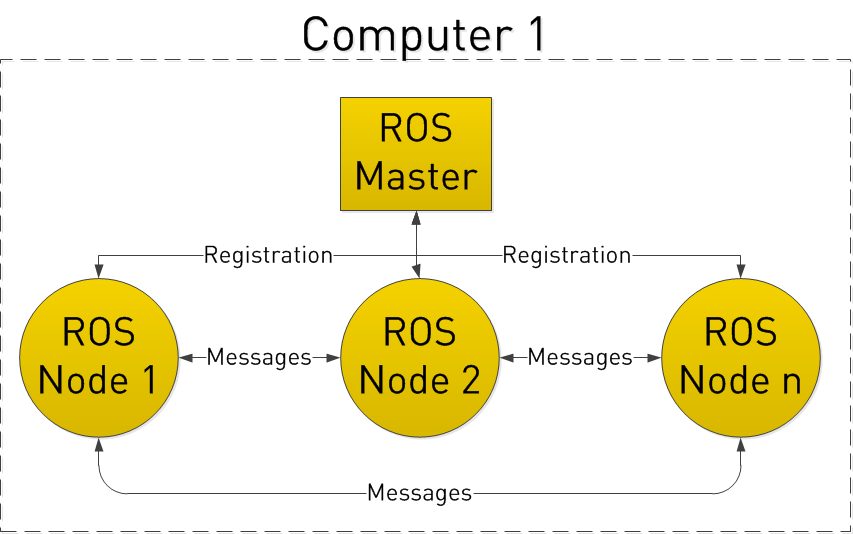
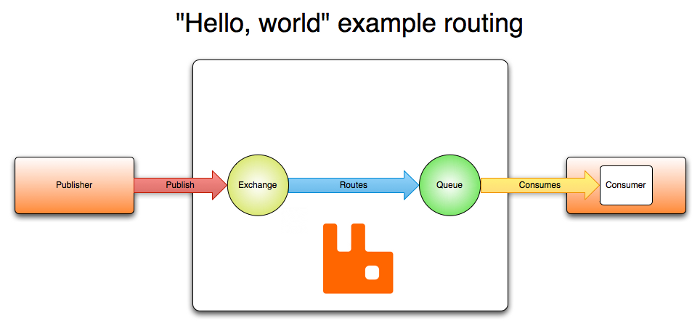
There’s a lot of article on the internet talking about message queuing architecture, so i won’t go into the message queuing architecture detail here.
In case of ROS, there’re two types of node : ROS Node and ROS Master. ROS Node is process that do simple task such as read data, processing data, etc. ROS Node can talk to each other by sending message through Topics. Each ROS Node can act as Publisher, Subcriber or both. ROS Master is the root process that work as a look up table. By using this look up table, we can exchange message between each node without worrying about node’s specific detail and address.
If you’re fammiliar with message queuing architecture (RabbitMQ), you’ll find this similar word comparing table useful. The Publisher/Subcriber used in ROS mean that message from 1 Publisher can be used by many Subcriber.
| RabbitMQ | ROS |
|---|---|
| ROS Master | RabbitMQ |
| ROS Node | Publisher/Subcriber |
| Topics | Message queue |
| Message | Message |
Let’s go deeper to understand how these concepts work in the following case :
1. Camera is connected to robot Arm
2. Robot read camera data and do simple image processing
3. Dev-PC (Laptop) read camera image and display it
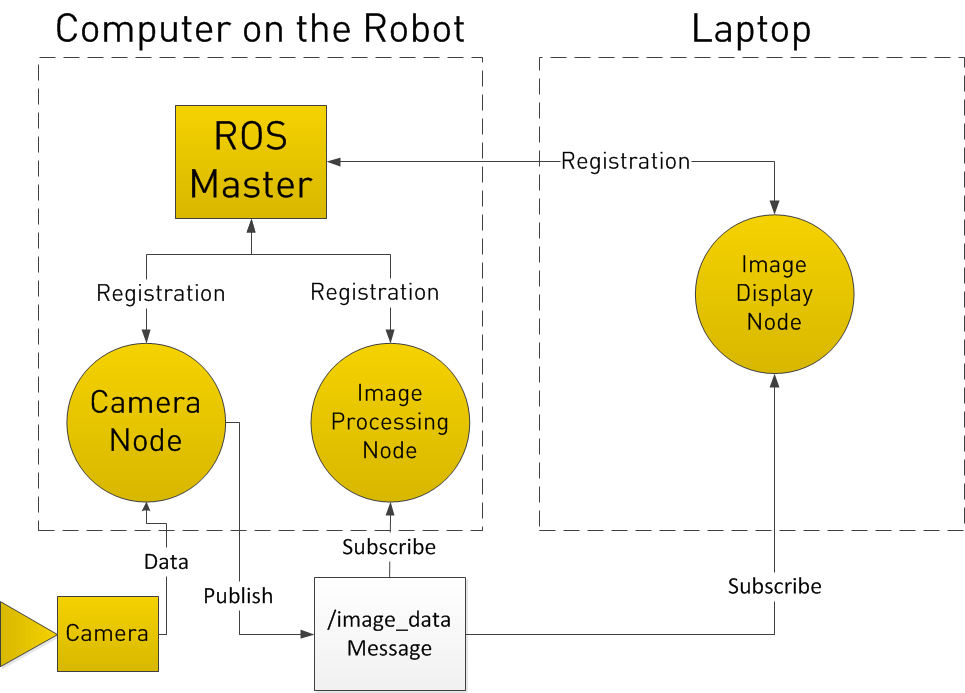
The development process should be as follow:
1. Start the ROS Master
2. Start Camera Node, Image Processing Node, Image Display Node
3. The un-stopped loop
a. Camera Node which read data from Camera then publish
image data into topics called /image_data
b. Image Processing Node and Image Display Node subcribe from /image_data topics and consume the message
In the next post, i’ll go into further detail about how to write ROS program and how to use image processing program with ROS.
1.4. Reference
以上
Leave a comment